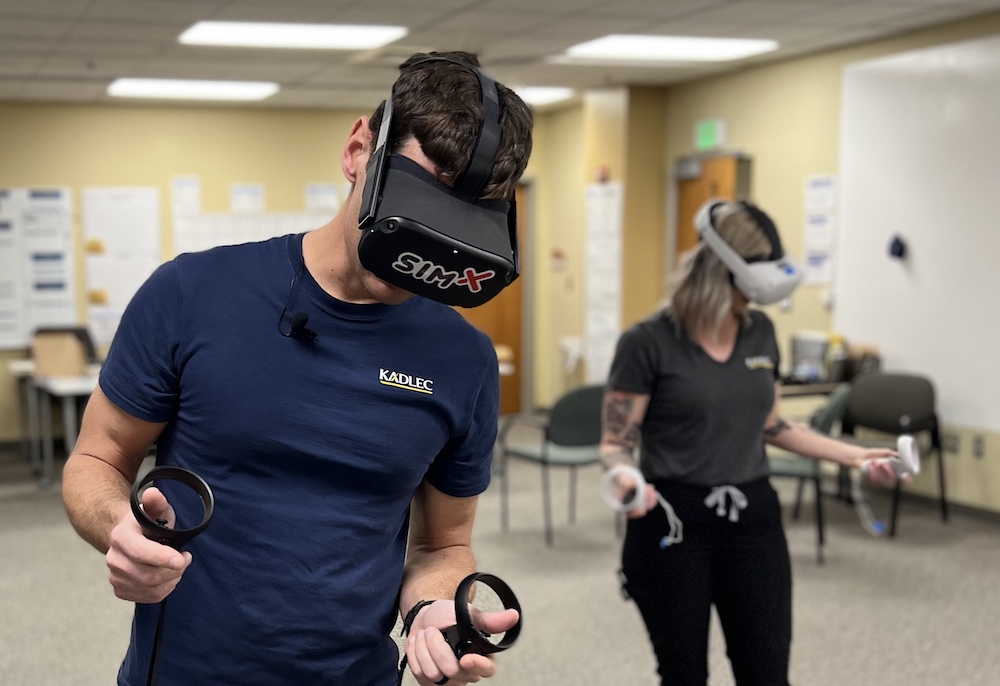
SimX is completely changing the way healthcare simulation training is conducted. For decades, patient manikins have evolved to incorporate varying degrees of sophistication paired with back-end technology to enhance the medical simulation experience. While effective, the clinical simulation manikins require a significant initial investment, as well as comprehensive staff training and maintenance costs. Rather than continuing to support physical manikins, SimX has successfully replaced physical manikin training with virtual patient encounters through customizable Virtual Reality (VR) scenarios.
SimX Presents Virtual Manikins
A rigid plastic manikin lacks the ability to provide truly realistic patient encounters, is inconvenient, and costs magnitudes more than VR training. Yet, without the manikins that have been relied upon for decades, what’s the alternative? SimX has over 250 virtual patient encounters that learners can choose from. In partnership with any given customer, SimX also creates custom VR scenarios. If that’s not enough, SimX partnered with Elsevier to create the biggest library of VR nursing simulation scenarios in the world.
Along with the extensive off-the-shelf library, in 2022 SimX released the first in a series of Virtual Manikins that mimic a physical manikin experience. Unlike the manikins we know, SimX’s virtual manikins can be quickly modified and customized to meet the needs of learners and educators alike.
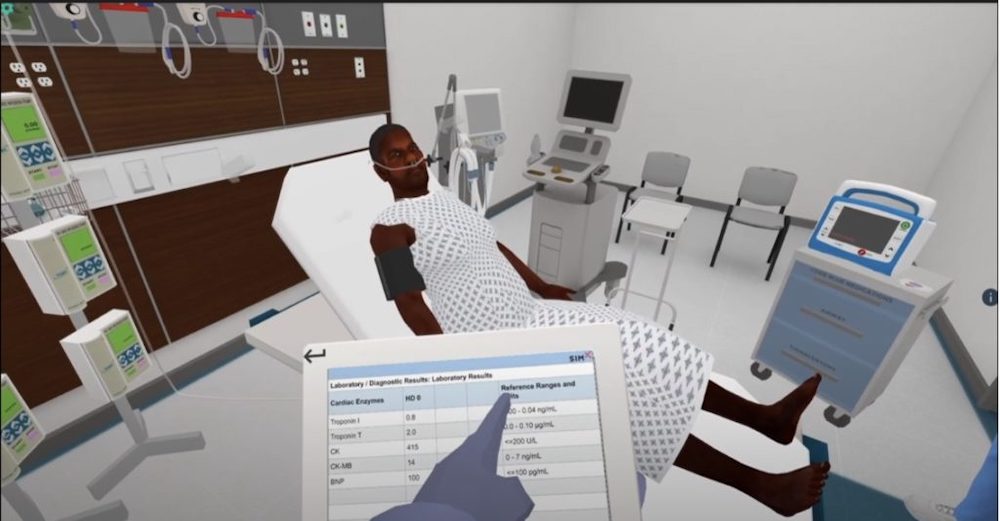
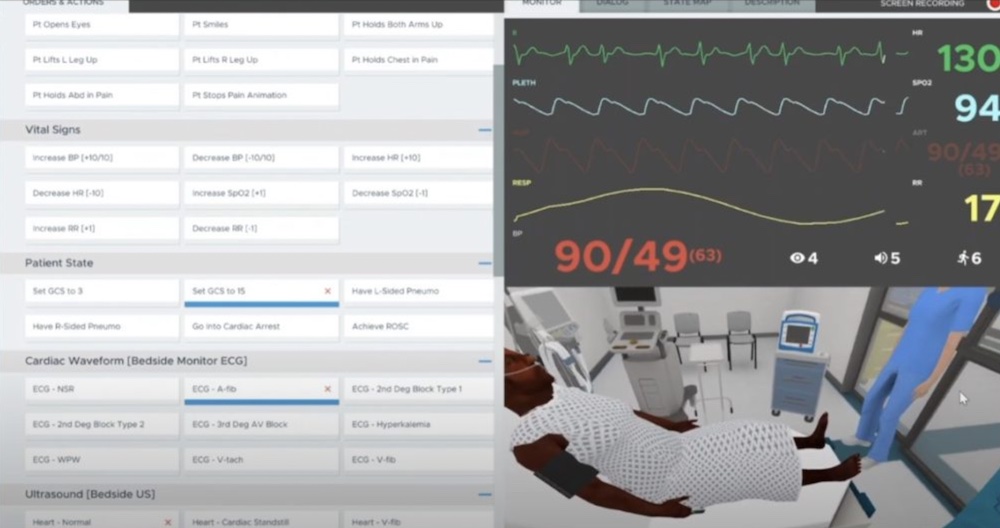
Whereas a physical manikin has a limited set scenario that a learner must assess and solve, the virtual manikin sim can be modified in real-time. Facilitators can control the manikin’s vitals, exam results, final diagnosis, and even various manikin animations with the push of a button. For example, a SimX chest pain VR manikin can be made to feel sudden angina and grip their chest.
A facilitator can then change cardiac rhythms on the monitor, EKGs in a virtual EMR, and even modify a tactile pulse. More than that, they can move between giving the manikin chest x-rays and live ultrasound images to reflect a pneumothorax, CHF, or pneumonia.
Then, the SimX Virtual Manikin series allows facilitators to respond in real-time to what learners need as they navigate the scenario and react to any prompts, events, or NPC dialogue. Instead of a fixed manikin with a lengthy set-up and limited options, the SimX virtual manikin sim series allows learners and educators to create different scenarios, diagnoses, and treatment options all with less than five min of setup. Here’s to making virtual a reality!
Any Patient, Any Tool, Any Environment
Virtual Reality (VR) scenarios have the ability to revolutionize healthcare simulation in a number of ways. While high-fidelity manikins have come a long way in terms of realism, they are still severely limited as plastic/silicone robots. A medical manikin being able to emulate neurological deficits such as unilateral weakness or dynamic facial droop is impossible. A manikin cannot break out in hives or a desquamating rash.
Users will never have a manikin pacing around the room while trying to sign out of your hospital against medical advice or have a grand mal seizure followed by hematemesis. The inflexible nature of manikins means they’ll never reach the level of realism required to truly recreate a clinical patient encounter.
Along with the manikins themselves, traditional medical simulation requires a large number of associated medical tools and devices. By the time users scavenge ventilators, chest tubes, medication vials, drapes, cardiac monitors, code carts, etc., they will realize the cost of a fully simulated environment. Of course, in VR, such a problem is nonexistent.
Learners can use any tool necessary for any patient, and have immense freedom in custom VR sims to assess patients, find the right tool, and experience various virtual environments. They may find themselves in an ED, OR, a patient’s home, an office, or anywhere else where they may have to treat real-life patients. Training no longer needs to be a singular, static experience but can be customized to fit the needs of both learners and educators.
Unlike manikins, patients in virtual reality can be made to reflect true-to-life demographics with varying symptoms, physical exam findings, and psychosocial stressors. Rather than a static body on a table, learners interact with dynamic characters to gain and retain knowledge far better than many other training techniques. Studies have shown that VR is more effective than other training solutions at improving knowledge and enhancing student engagement, immersion, and training efficiency (references below).
Effective Healthcare Simulation, Without The Robots
With the rise of VR medical simulation training, manikin sim centers can be expanded to train in an office, a bedroom, or any spare room/space available. All the learner needs is a capable headset and SimX patient encounters. Transitioning from a physical space to a virtual one truly makes an “anytime, anywhere” educational experience possible.
For example, in VR, multiple players can join the same virtual space at any time for lectures, special demonstrations, or group training scenarios. The SimX system allows for non-co-located team training, meaning that team members are not required to be in the same physical space for them to share the same virtual space. Guest lecturers, fellow learners, and facilitators can all be in different locations–different countries, even–and still learn and train together.
40% Less Than the Cost of Manikins
Additionally, another benefit of VR training is that the practice requires less maintenance, equipment, and manpower. This not only saves on essential space and time but is reflected in very real cost savings. The calculated cost of virtual reality simulation was found to be 40% less than high fidelity sim (reference below). Note, this figure doesn’t include the cost of replacing physical manikins when they inevitably degrade. With comparatively minimal setup and maintenance costs, VR is far less expensive than manikin sim programs.
More About SimX
SimX, previously called SimXAR, is a healthcare software company specializing in medical simulation, virtual reality, augmented reality, and medical training and education. The company brings virtual and augmented reality into the realm of healthcare simulation and training. SimX was founded by physicians in training at Stanford, the University of California at San Francisco, and the University of California at Los Angeles.
They understood that simulation practice and training are extremely beneficial to both learners and clinicians, and hoped to use virtual reality to make simulation cheaper and more accessible, to ultimately reduce medical error and increase patient safety. Seeking to push simulation forward, SimX developed a software system that was the first comprehensive professional-grade VR medical simulation system product available on the market.
Founded in 2013 and headquartered in Mountain View, California, the platform allows medical teams to replace expensive manikins with incredibly flexible simulated patients, backed by a robust case creation engine.
Learn More About SimX
[toggles behavior=”toggle”]
[toggle title=”References:“]
- Yu, M., Yang, M., Ku, B., & Mann, J. S. (2021). Effects of Virtual Reality Simulation Program Regarding High-risk Neonatal Infection Control on Nursing Students. Asian Nursing Research, 15(3), 189–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anr.2021.03.002
- Chen, F. Q., Leng, Y. F., Ge, J. F., Wang, D. W., Li, C., Chen, B., & Sun, Z. L. (2020, September 15). Effectiveness of virtual reality in nursing education: Meta-analysis. Journal of Medical Internet Research. JMIR Publications Inc. https://doi.org/10.2196/18290
- Lebdai, S., Mauget, M., Cousseau, P., Granry, J. C., & Martin, L. (2021). Improving Academic Performance in Medical Students Using Immersive Virtual Patient Simulation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of surgical education, 78(2), 478–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsurg.2020.08.031
- Bumbach, Michael D. PhD, APRN, FNP-BC, RN; Culross, Beth A. PhD, RN, GCNS-BC, CHSE; Datta, Santanu K. PhD. Assessing the Financial Sustainability of High-Fidelity and Virtual Reality Simulation for Nursing Education: A Retrospective Case Analysis. CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing: September 2022 – Volume 40 – Issue 9 – p 615-623
[/toggle]
[/toggles]