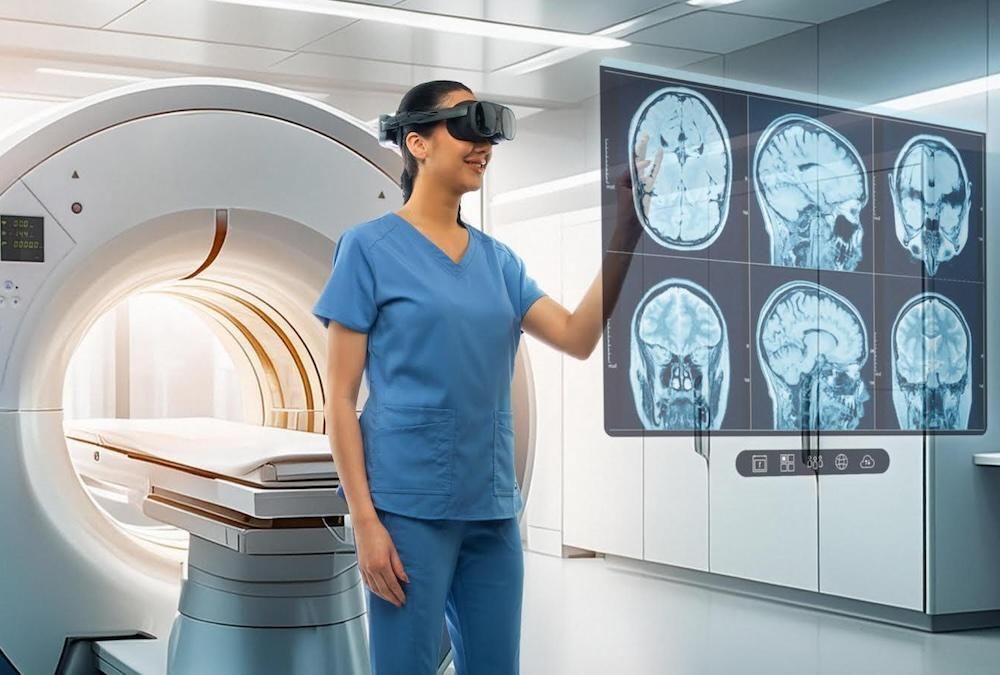
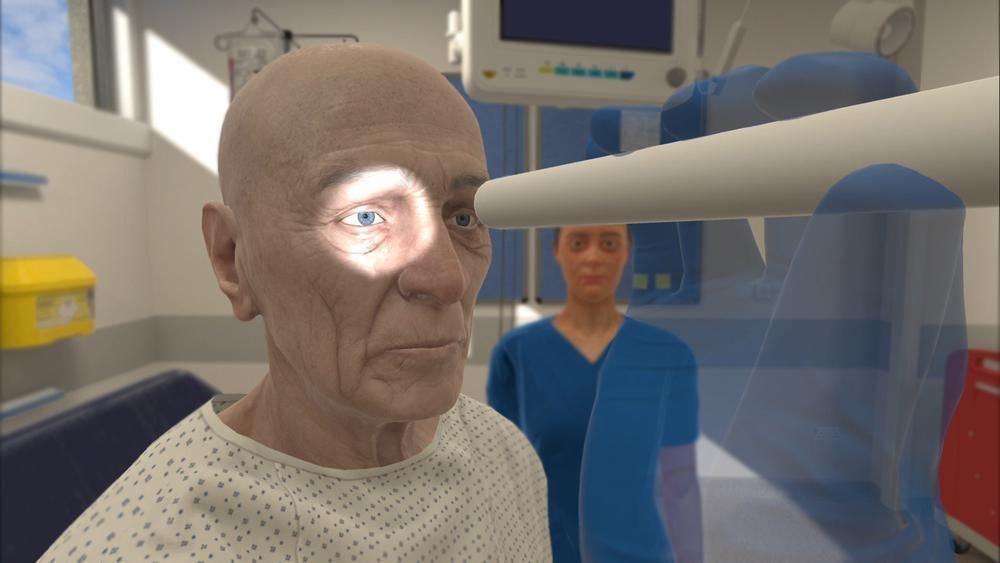
Orthopedic surgery is no game. Get it right, and a patient’s life can be transformed for the better. Get it wrong, and they could end up worse off than before you started. So how are two former game developersvirtual reality and an orthopedic surgeon working together to more effectively train practitioners? Today we share some interesting excerpts of recent article from the Unreal Engine’s blog on how Precision OS delivers accredited curriculum for orthopedic surgical training in VR!
Formed in a Vancouver basement two years ago, Precision OS is now a flourishing business that provides orthopedic surgical training in virtual reality. Two of its three founders, CTO Colin O’Connor and Chief Creative Officer Roberto Oliveira, had both worked in the video game industry for decades. After years at Radical Entertainment, Black Box Games, and industry giant Electronic Arts they helped co-found United Front Games together, where they had critical and commercial success with titles like ModNation Racers and Sleeping Dogs.
In 2016, the pair were looking for something new to get their teeth into when they had what Oliveira describes as “a very random meeting” with orthopedic surgeon Dr. Danny Goel, now CEO of Precision OS. After a get-together at a local pub which included a demo from O’Connor of the newly released HTC Vive, the team started building a VR training platform for orthopedic surgery. Initial feedback from surgeons, residents, and device companies was positive, and the three went all-in and started the business.
For Precision OS’s VR training, the goal is to simulate the real environment as closely as possible, enabling students to experience what surgery looks and feels like. They encourage trainees to make mistakes in simulation—without putting patients at risk. To familiarize themselves with the procedures and thereby recreate them as closely as possible, Oliveira and O’Connor physically stand behind Goel and watch him operate. They also study medical books and actual cadavers. And then it’s a case of recreating what they have witnessed in a real-time VR environment.
Having had experience with several game engines in the past, including writing their own at United Front, Oliveira and O’Connor chose Unreal Engine. “I know for a fact that Unreal supports more things out of the box than any other engine out there,” says O’Connor, explaining the choice. “And I wanted to make sure that we hit that triple-A fidelity mark right from the outset.”
The accuracy of the simulation is particularly important when dealing with surgery, where a misrepresentation could have significantly grave consequences. Oliveira and O’Connor use every trick they’ve ever learned in game development to make sure they are able to represent each step as faithfully as possible, and Unreal Engine’s deep and broad feature set is part of the solution.
“With the power behind the Blueprint system, the animation system, support for morph targets, vertex animation…Unreal just gives us an array of technology that we can hook into to solve these problems of recreating a medical environment,” says O’Connor. “There are ethical considerations to what we are building,” says Goel. “Misrepresentations and over-optimism of VR are critical elements when creating something with consequences to actual patients. We are sensitive to both and are researching all aspects of virtual reality. A second and important element to also consider is the point about empathy. It is important for the trainees to remember how their practice has implications to patient lives.”
As well as the visual aspect, the application features auditory feedback, so that you can hear the anesthetic machine, or the sound of a drill or mallet as you use it. And haptics are also employed, but only where they are critical to support the training. Goel explains that it’s the ability to make decisions during the training, and to make mistakes, that forms their double-loop simulation experience inherent in what Anders Ericsson has coined “deliberate practice”. “The decisions you make prior to and during surgery are how we impact patient outcomes,” he says. “This decision-making process is what we embed within our simulation modules.”
Overall, as the technology becomes more affordable, accessible, and portable, it is seeing wide acceptance. The fact that the system can also be used to collect performance data and provide metrics for the students on the backend is another clear benefit to those whose mandate it is to train and educate the next generation of surgeons.
Today, Precision OS modules are in use by hundreds of residents in the ten North American universities and institutions that were their original partners, and, in conjunction with their other customers, are also available in in countries as far apart as Japan, Switzerland, France, and Australia. With their product for the international organization known as the AO Foundation and a new preoperative planning tool, they plan to educate thousands of people from North America, and then tens of thousands globally.
In May of 2019, Precision OS received accreditation from a provider to the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada, enabling their training to be used as the performance appraisal component of continuing medical education (CME) for surgeons. This accreditation, coming as it does from a highly regarded organization, is a validation of the company’s efforts to achieve the highest-quality training through VR.
About the Unreal Engine 4
Unreal Engine 4 is a complete suite of development tools made for anyone working with real-time technology. From enterprise applications and cinematic experiences to high-quality games across PC, console, mobile, VR and AR, Unreal Engine 4 gives you everything you need to start, ship, grow and stand out from the crowd. A world-class toolset and accessible workflows empower developers to quickly iterate on ideas and see immediate results without touching a line of code, while full source code access gives everyone in the Unreal Engine 4 community the freedom to modify and extend engine features.
About Epic Games
Founded in 1991, Epic Games is the creator of Fortnite, Unreal, Gears of War, Shadow Complex, and the Infinity Blade series of games. Epic’s Unreal Engine technology brings high-fidelity, interactive experiences to PC, console, mobile, AR, VR and the Web. Unreal Engine is freely available.
Read the Entire Article on Precision OS Surgery Training in VR Using the Unreal Engine Here!
Today’s article was guest authored by Seb Loze, Simulation Industry Manager at Epic Games. Have a story to share with the global healthcare simulation community? Submit your simulation news and resources here!